Plantar fasciitis is a common ailment, affecting over 2 million people in the United States alone, as reported by the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. Those with plantar fasciitis tend to experience regular, sharp pains in their heel, especially after long periods of inactivity (i.e. after a long night’s sleep or when getting up from a seated position after being off of their feet for hours). This pain may fade as they walk around and use the affected foot, but it’s a consistent problem that reappears on a regular basis and makes it difficult to carry out daily routines. There are numerous treatment options available for plantar fasciitis varying from simple pain medications like Ibuprofen or Acetaminophen to surgically detaching the plantar fascia from the heel bone. However, even if your case is severe enough to consider such drastic surgery, there may be another alternative available for you called Shockwave Therapy.
What is Plantar Fasciitis and How is it Diagnosed?
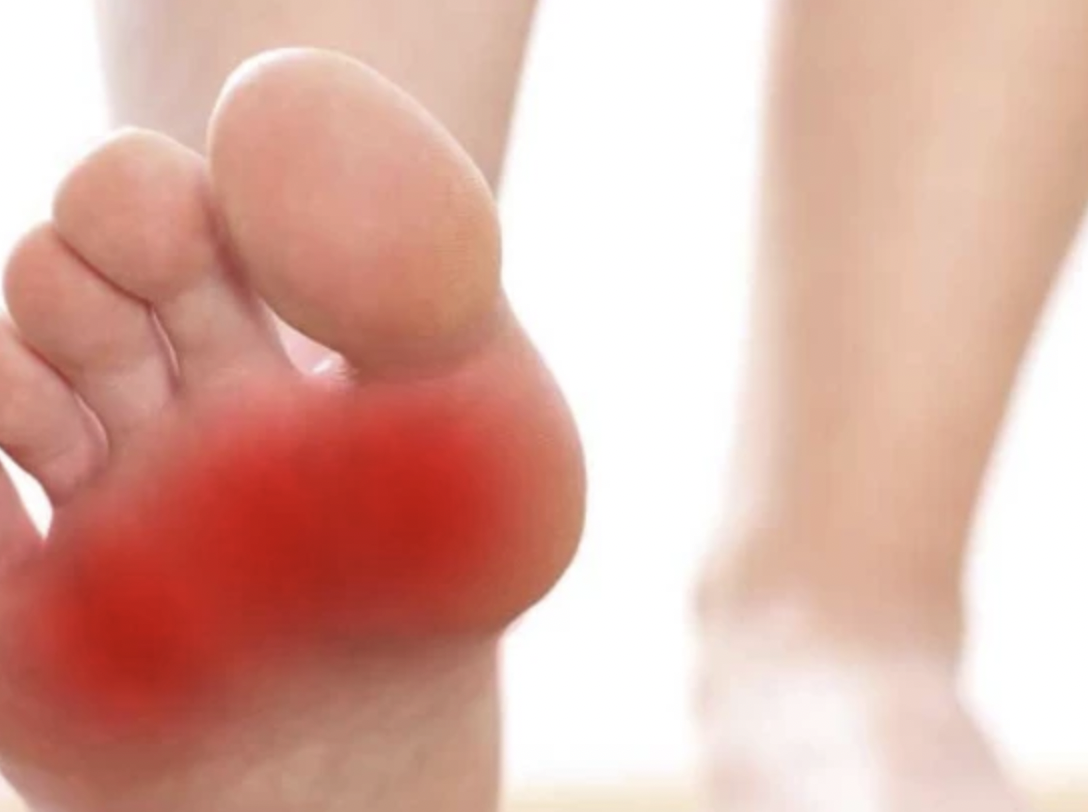
Plantar fasciitis describes the painful inflammation of a stretch of tissue on the bottom of your foot that connects your heel bone to the ball of your foot and toes. That inflammation makes it difficult to walk or flex your foot without experiencing sharp, stabbing pain throughout the arch of your foot and impedes your ability to complete menial tasks.
Generally speaking, the condition is diagnosed by determining where your pain is, what kinds of activities or at which times you notice the pain flaring up, and if things like massages or continued activity seem to alleviate said pain. If you’re answering that the pain tends to flare whenever you first get up in the morning or when standing up after being seated for a long period of time, chances are high you’ll be told you have plantar fasciitis.
What Kinds of Factors Increase Your Risk for Plantar Fasciitis?
While there is no known specific cause of this condition, there are several related factors or conditions that may contribute to how quickly you develop plantar fasciitis and increase the frequency of the pain. Such factors may include:
- Obesity
- Shoes without proper arch supports
- Having an unusually high arch and not using inserts
- Long periods of stationary standing time
- Running too often or engaging in other high-impact sports or exercises
- General overuse of your feet from walking, standing, running, etc.
Granted, moderate to regular amounts of exercise with proper arch supports should not cause plantar fasciitis or contribute to it becoming chronic. On the contrary, routine exercise with supportive shoes should help keep that band of tissue properly flexible without overworking it or inflaming it.
What if Pain Medications, Therapy, and Massages Don’t Work?
The pain caused by plantar fasciitis can be stubborn and intense. For many, over the counter pain medications, icing the area, and gentle massaging may be enough to alleviate the pain in the beginning stages, but as it’s left untreated and the pain becomes more frequent, most find that such simple methods cease to make a difference. Therapy is often recommended for those experiencing moderate to severe pain, especially if the next available option is surgery.
If none of the above options work, your doctor may recommend surgery to detach the inflamed tissue from your heel bone, thereby relieving the tension in your foot and preventing further inflammation. However, this procedure carries its own set of risks (though it is successful for many), and there’s still a viable option available to you called Shockwave Therapy.
What is Shockwave Therapy?
Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy (ESWT) is a method of pain relief that involves sending gentle waves of energy into an affected area from the outside (hence “extracorporeal” – outside of the body) to quickly and effectively relieve pain. These energy waves help improve blood flow to the affected area, increasing the number of healing components available (such as platelets) to repair microscopic tears in the fascia or tend to inflammation.
As the treatment is applied from outside of the body, ESWT is a noninvasive alternative to surgery, which can have a range of damaging side effects that actually wind up weakening your foot instead of improving its condition. ESWT is also the only FDA-approved noninvasive treatment device for plantar fasciitis, has little to no downtime, and has had more impressive results than most other treatment options for this condition.
How Does ESWT Work?
Because the underside of your foot–specifically your heel–tends to get less blood flow than the rest of your body, fewer healing components are available to repair damages or improve the condition of the area, meaning that injuries or trauma take significantly longer to heal. Using the energy of sound waves, ESWT can dramatically stimulate blood flow to the application area, increasing the heel’s supply of platelets and other reparative properties within your blood.
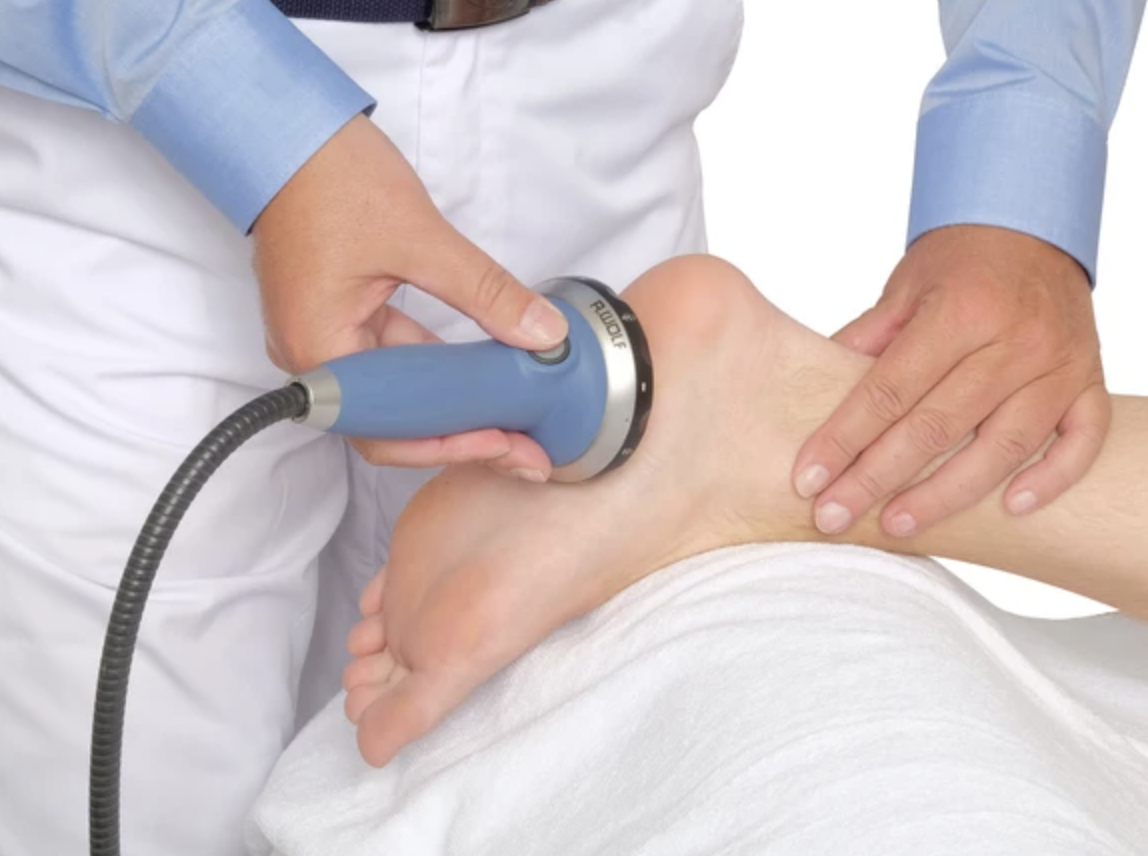
The application process itself involves using a probe to send those energy waves into your skin (without being invasive). Your doctor will mark the most tender spots on your heel with a marker, indicating the inflamed area that needs to be treated. They will then apply a protective, conductive gel to your skin to maximize the effectiveness of the sound waves, followed by the actual shockwave treatment of the fascia with the probe by touching it to your skin. The shockwave itself is audible and tangible, but quick and easy. After treatment, your doctor will clean any gel off of your foot and see how you’re responding to the shockwave treatment.
All in all, the procedure should not take longer than 20 minutes and should yield immediate and effective results! Typically, more than one treatment spaced apart by a few weeks is necessary (the average number of treatments is 4), but many patients find that one treatment is enough to improve their condition for quite a while. So, before you commit to any invasive surgeries or permanently altering procedures that carry risk of further damage, consider asking your doctor about Shockwave Therapy to see if you may be a candidate. The treatment is significantly safer than surgery and often just as effective, if not more.